Upcycler
Introduction to the Thinkwise Upcycler
The goal of the Thinkwise Upcycler is to jump-start the modernization of your existing legacy application. Depending on your legacy technology, 20% to 50% of the development time will be saved by using the Upcycler.
The Upcycler completely replaces the legacy application and migrates its data automatically to the new RDBMS of your choice. It can use AI and other technologies to enrich your legacy application during the process. The modernized application has a fully responsive web app user interface and an integrated service tier. After having upcycled your legacy application, you can further develop your new application.
The Upcycler is for advanced users only. For a successful replacement of your legacy application, you will need a team with the expertise of your application, your legacy technology, and the Thinkwise Platform. Please contact Thinkwise or a Certified Partner for more information.
The Thinkwise Upcycler comes with Upcyclers for a large number of relational databases. For an overview, see Available Technology Upcyclers.
- All Upcyclers can be tailored to suit your specific needs.
- It is possible to develop and use your own Upcyclers for other technologies.
Thinkwise Upcycler installation
The Thinkwise Upcycler is a separate application within the Thinkwise Platform and should be deployed as such. It should be downloaded as part of the platform installation package and deployed through the Thinkwise Deployment Center.
For more information, see the Thinkwise Deployment Center manual.
Set up AI integration
AI greatly enhances the Upcycler's enrichment capabilities. You can use AI enrichments to, for example, add comments to existing code, add descriptions for any object in the model, or replace existing code concepts with new ones.
To enable AI in the Upcycler, see Enable generative AI for the Thinkwise Platform.
An overview of the upcycling process
-
Metadata - The first step is to derive as much metadata as possible from your legacy application. Doing this right at the start of your upcycle project saves an enormous amount of time later. Thinkwise provides a separate utility program for this, the Thinkwise Extractor. It extracts the metadata from your legacy application and puts it into a file that can be read by the Thinkwise Upcycler. For some legacy technologies, you can use the export facilities of that technology instead.
-
Conversion - The next step is to convert your source's metadata into metadata for the Thinkwise Software Factory with the help of an Upcycler. An Upcycler contains a series of steps at three levels, implemented in SQL. The levels inherit their steps from each other.
-
Generic level - This level consists of generic upcycle steps and generic data import steps that have been defined by Thinkwise and cannot be modified. It gives you an easy start in creating your own Upcycler if one is necessary. For more information, see Generic upcycler.
-
Technology level - The Thinkwise Upcycler comes with several ready-made technology-specific Upcyclers that cannot be modified. If no upcycler is available for your legacy application's technology, you can create your own Technology Upcycler. A Technology Upcycler consists of a technology definition, upcycle steps, and data import steps. The Technology level inherits its steps from the Generic level. For more information, see Available Technology Upcyclers and Create your own Technology Upcycler.
-
Application level - At this level, you can tailor your Technology Upcycler for upcycling a specific legacy application. It consists of an application definition, upcycle steps, and data import steps. The Application level inherits its steps from the Technology level. For more information, see Fine-tune an Upcycler for your application.
-
-
Data import - The next step is the Data Importer. This process is structured in the same way as the Upcycler process.
-
Enrichment - The final step is Enrichment. This process is structured similarly to the Upcycler process, but each step performs an analysis that delivers proposed actions you can select and apply.
Extract the metadata from your legacy application
To upcycle an application, you first need to extract the model and the data from your legacy application. Usually, the extraction is performed by either the Thinkwise Extractor or the export functionality of your legacy platform. For more information on the export functionality, see the Technology Upcyclers.
The Thinkwise Extractor is a command-line utility for extracting the model and data from legacy applications.
It consists of one executable and a folder containing some scripts. This makes it easy to use, even when no Thinkwise installation is available yet. Scripts for all supported technologies are pre-delivered.
Use the 32-bit version of the Thinkwise Extractor if you have a 32-bit data source and the 64-bit version if you have a 64-bit data source.
To use the Thinkwise Extractor:
- Copy the executable and the scripts to a computer with access to the legacy database.
- Run
twupcycle.exefrom either the win-x86 or the win-x64 folder, using the appropriate command line parameters.
twupcycle.exe <COMMAND> <ACCESS METHOD> <OPTIONS>
| COMMAND | |
|---|---|
| schema | Extract the schema of a datasource. |
| data | Extract the data of a datasource. |
| ACCESS METHOD | |
|---|---|
| odbc | For now: always odbc. |
| OPTIONS | |
|---|---|
| -h, --h | Prints help information. |
| --dsn | The DSN (Data Source Name) of the connection. Required, unless -c, --connection-string has been specified. |
| -c, --connection-string | The string for connecting to the data source. Required, unless --dsn has been specified. |
| --uid | Option to explicitly set the user name for the connection string. |
| --pwd | Option to explicitly set the password on the connection string. If no --uid has been specified, this option is ignored. |
| -e, --extractor | This can be either a zip file or a directory containing script entries under a schema/odbc path relative to the root. - If you enter a relative path, the Extractor will try to find a match in the current directory and the location of the program. - The default extension of an archive is .extractor. - A path with an extension will always try to look for a zip file with the specified extension instead of .extractor. For example, --extractor mssql will try to find an extractor archive in the following order:-- <current working directory>/mssql.extractor -- <current working directory>/mssql -- <program location>/mssql.extractor -- <program location>/mssql If this option has not been specified and the input has not been redirected, the Extractor will show a list of .extractor files to choose from, if it detects any. |
| -o, --output-file | The file path where the output file(s) should be written. - For the schema command, you will be prompted for a path if this option has not been specified, unless the output has been redirected (e.g., due to a pipe).- For the data command, by default, the files will be written to the current working directory.- Relative paths will be considered relative to the current working directory. - Output is always written using UTF-8 encoding with a byte order mark (BOM). |
Examples
Here are some examples for extracting schema and data. You can adapt them to your own needs or write your own lines.
This example extracts the schema from an MS SQL Server database. Here, it contains --connection-string. This can be replaced by --dsn.
twupcycle.exe schema odbc --connection-string "Driver={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server};Server=MyServer\MyInstance;Database=AdventureWorks2019;Trusted_Connection=yes;" --extractor mssql --output-file schema.json
This example extracts the schema from a MySQL database.
.\Extractor\twupcycle.exe schema odbc --dsn MySQL_local --extractor .\Extractor\Scripts\MySQL --output-file schema.json
This example extracts the schema from an Oracle database.
..\Extractor\twupcycle64.exe schema odbc --dsn OracleDSN --uid ******** --pwd ******** --extractor oracle --output-file .\schema\schema.json
This example extracts the schema from an DB2 database. Note that the default folder for the extractor has been changed here. You can add a user name and
password with --uid myuser and --pwd mypassword. If you only add a user name (--uid my user), the user will be prompted for the password.
twupcycle.exe schema odbc --dsn DB2Thinkwise --extractor .\Scripts\DB2 --output-file schemaDB2.json
This example extracts the data from a ProgressOpenEdge database:
twupcycle.exe data odbc --dsn ADTEST99ZZ --uid myuser --pwd mypassword --extractor .\Extractor\Scripts\PROGRESS --output-directory .\Data
This example extracts the data from a PostgreSQL database:
twupcycle64.exe data odbc --connection-string "Driver={PostgreSQL ODBC Driver(UNICODE)};Server=localhost;Port=5432;Database=dvdrental;" --uid myuser --pwd mypassword --extractor postgresql --output-directory .\data
This example extracts the data from a MySQL database:
twupcycle.exe data odbc --dsn MySQL_local --extractor .\MySQL --output-directory .\Data
This example extracts the data from an Oracle database:
..\Extractor\twupcycle64.exe data odbc --dsn OracleDSN --uid ******** --pwd ******** --extractor oracle --output-directory K:\temp\oratestdata\
Add the file storage location path in IAM
If you use a file system as the File storage type, make sure that the file storage location path in IAM is set correctly before proceeding to the Upcycler.
menu Authorization > Applications > tab General settings > tab File storage locations
- Select the file storage location in the list on the left.
- On the tab File storage location, click Edit
.
- In the group Options, enter the Path to your file storage location.
Upcycle your application
1. Create an application in the Thinkwise Upcycler
After extracting the model and data from your legacy software and setting the file storage location path, add an application to the Thinkwise Upcycler:
menu Upcycle > Applications > tab List
- Click Add
.
- In tab Form, enter the required information about the application, the source model, the source data, the target model, and the target application database:
| Application | |
|---|---|
| Field | Description |
| Name | The application's name in the Thinkwise Upcycler. |
| Technology | The legacy technology in which the application was build. |
| Active | Inactive applications will not be shown by the default prefilter. |
| Source model | |
|---|---|
| Field | Description |
| Source model | Preview field for a part of the source model, once it has been imported. |
| Model file type | Type of data in the model file, gets a default value from the Technology level. |
| Model file extension | File extension of the model file, gets a default value from the Technology level. |
| Model file encoding | Encoding of the model file, gets a default value from the Technology level. |
| Source data | |
|---|---|
| Field | Description |
| Data folder | Folder where the extracted data files will be saved. This has to be a folder on the webserver where Indicium is installed. |
| Data file type | Type of data in the data files, gets a default value from the Technology level. |
| Data file extension | File extension of the data files, gets a default value from the Technology level. |
| Data file encoding | Encoding of the data files, gets a default value from the Technology level. |
| Target model | |
|---|---|
| Field | Description |
| Model | Model ID that will be created for the upcycled application. |
| Branch | Branch ID (MAIN) that will be created for the upcycled application. |
| Primary application language | The language for which translations will be generated. For multi-language applications, this will be used as a fallback. |
| Model folder | Folder that will be used for your model. |
| SF database server | The database server on which your Software Factory is located. By default, this is the database server of the Thinkwise Upcycler. |
| SF database name | The name of the Software Factory database. |
| Target application | |
|---|---|
| Field | Description |
| Application database server | The database server on which your application database must be created. |
| Application database name | The name of the database that will be created. It will be used for importing your application data. |
If necessary: add languages
Some technologies support multi-language applications. If the matching Technology Upcycler supports it, you need to add the application languages. This will translate the language codes of your legacy application to the language codes of the Thinkwise Platform.
menu Upcycle > Applications > tab Form
- Add
the languages in the form on the right.
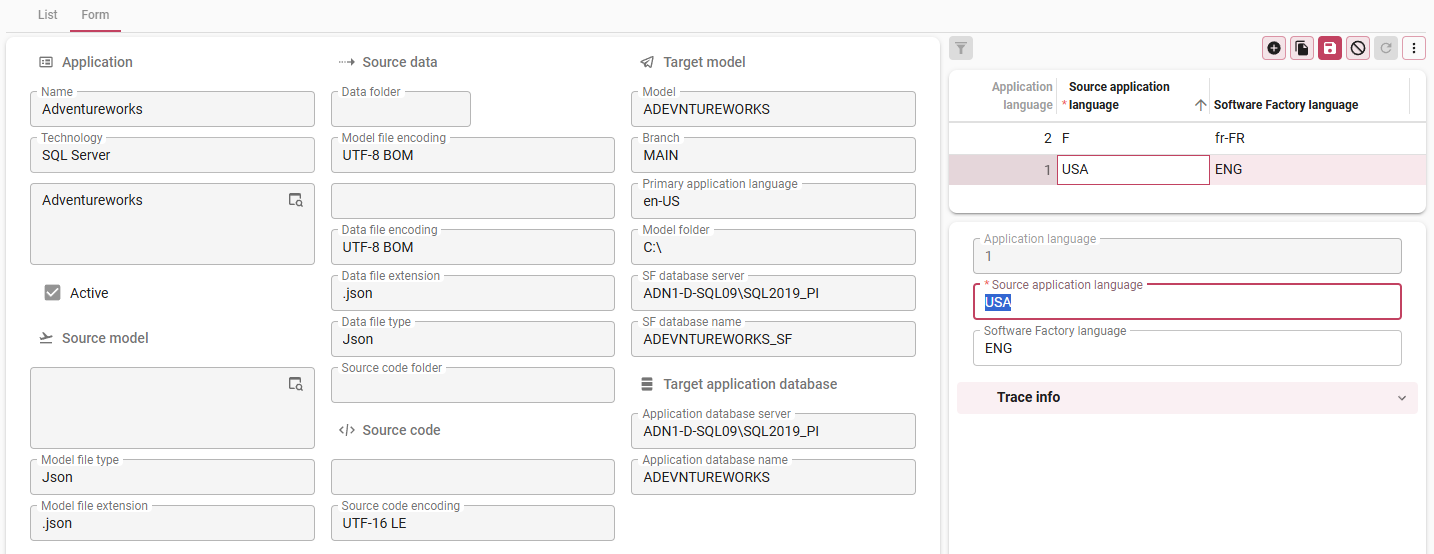 Form for adding a new application with multiple languages to the Upcycler
Form for adding a new application with multiple languages to the Upcycler
2. Import the source model
- Execute the Import source model
task to load the source model into the application.
After importing the source model, a preview of the model becomes visible in the Source model field.
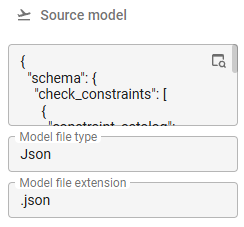 A preview of the model in the Source model field
A preview of the model in the Source model field
Now all information that your Upcycler needs has been entered into the Thinkwise Upcycler.
3. Execute the upcycle run
menu Upcycle > Upcycle runs > tab Application > tab Current
- Select your application.
- Execute the Execute upcycle
task.
This will execute the upcycle steps as defined in your Technology Upcycler. Where needed, it is overruled by steps at the Application level. In the Steps tab, you can track the progress.
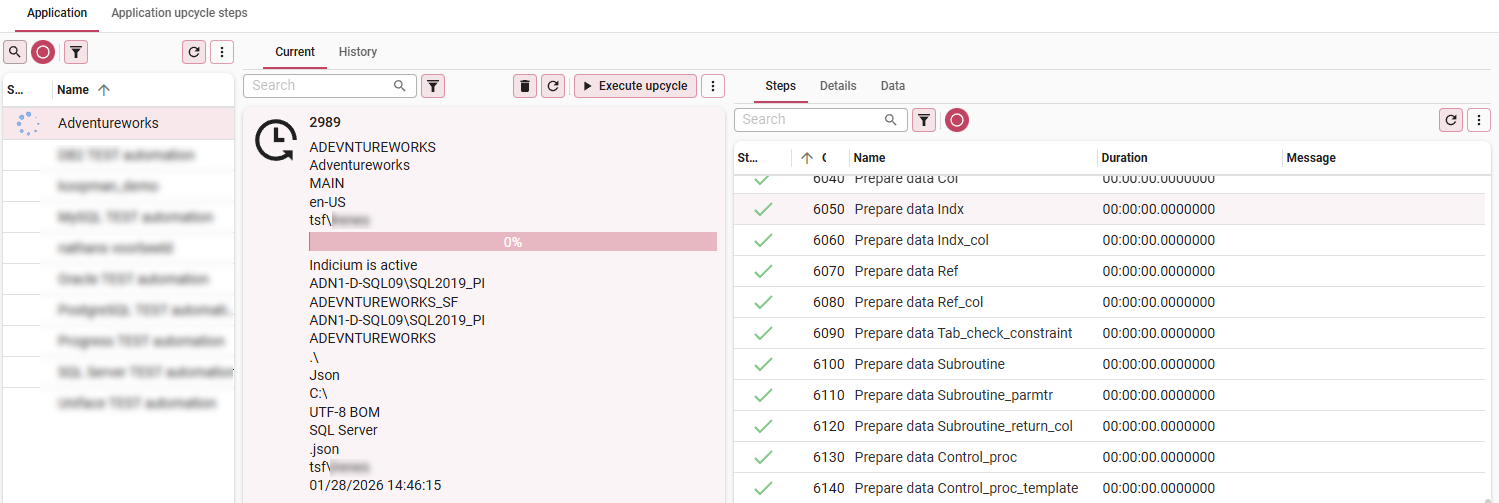 Progress of the upcycle run
Progress of the upcycle run
4. Inspect the upcycle run
menu Upcycle > Upcycle runs
After the upcycle run has finished, carefully inspect all messages to see if it is necessary to adjust the upcycle steps.
When at least the MODEL: Create model step was executed, a model has been added to your target Software Factory. If not all steps were successful, the model is incomplete. In that case, remove it, make the necessary changes to the Upcycler, and execute the Upcycle run again.
-
A list of all messages is available in tab Application > tab Current > tab Report:
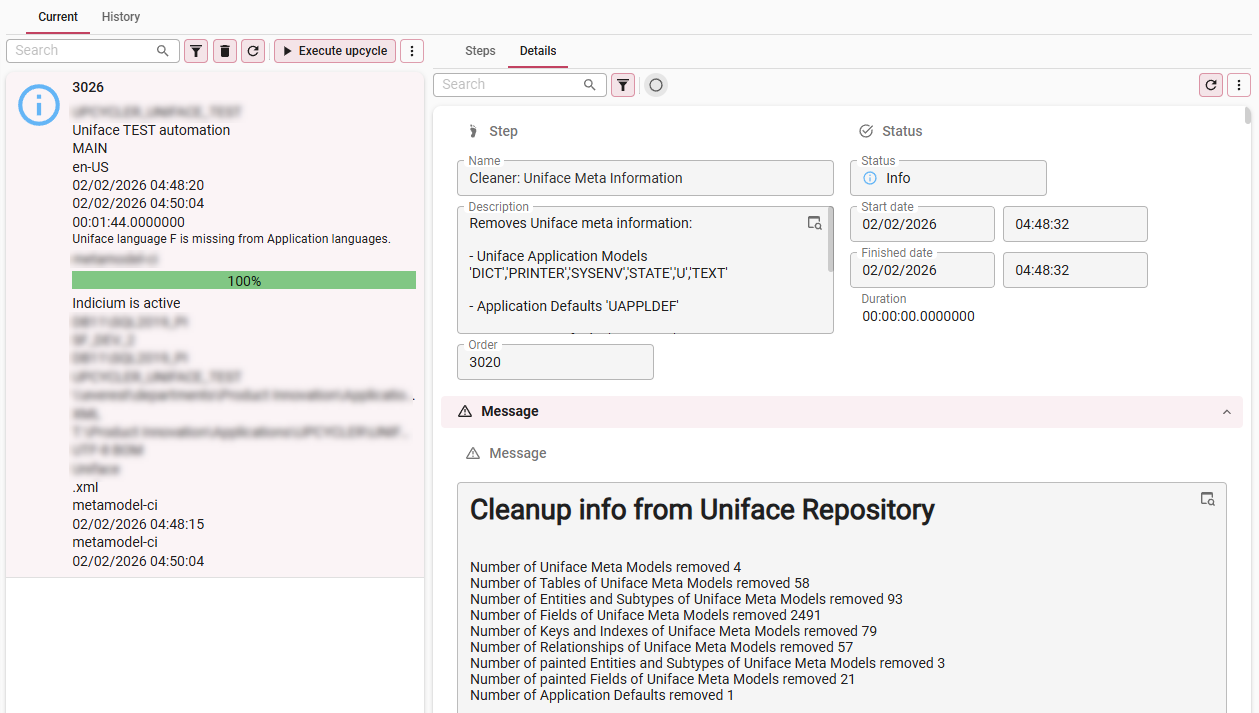 Messages in the Report tab
Messages in the Report tab -
To inspect the results in more detail, consult tab Application > tab Current > tabs Steps/Details:
Information message.
Error message.
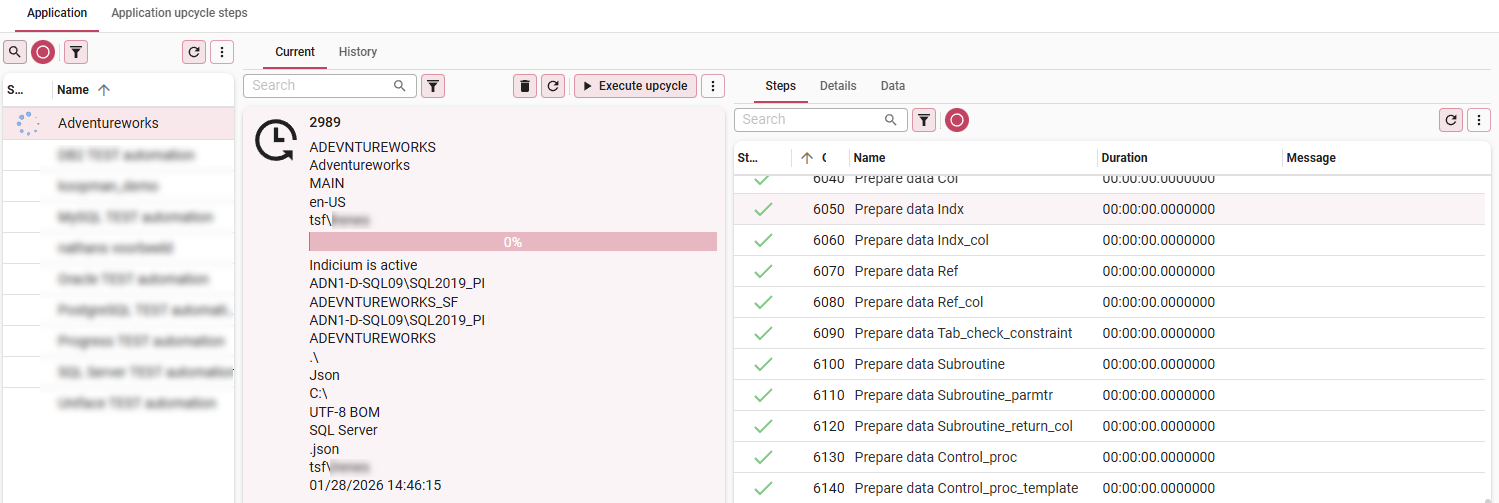 Inspect the results in more detail
Inspect the results in more detail -
To inspect what data was transferred to the Software Factory, look at tab Application > tab Current > tab Data:
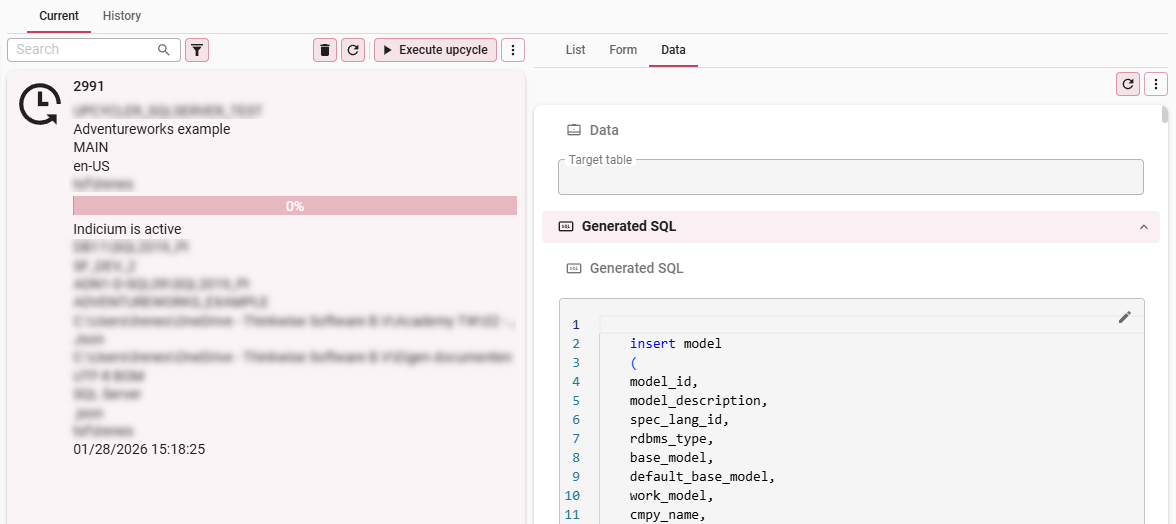 Transferred data in the executed upcycle steps
Transferred data in the executed upcycle steps
5. Inspect your application in the Software Factory
After a successful upcycle run, your new model will be available in the Software Factory. Take your time to inspect the result.
Do not make any changes yet, as you may want to fine-tune your Upcycler and run it again. Moreover, if you change the data model, you will not be able to import the data.
If you think the result is satisfactory, you can move on to the next step: Create your application.
6. Create your application in the Software Factory
In the Software Factory, create your application as usual, by running the Creation process.
- Run the Generate definition and Validate definition steps separately, so you can easily inspect the result.
- Check the messages carefully to see whether you can or need to fine-tune your Upcycler.
- If you think the result is satisfactory, you can run the Generate source code and Execute source code steps.
- If Execute source code is successful, you can start your application. At this stage, there is no data in your application yet.
7. Execute a data import run
menu Upcycler > Data import runs
- Select your application.
- Execute the Execute data import
task.
This will execute the data import steps as defined in your Technology Upcycler, where necessary overruled by steps at the Application level.
8. Inspect the data import
menu Upcycler > Data import runs > tab Application > tab Current > tab Steps
-
After the data import run has finished, inspect the information and error messages carefully to see if it is necessary to adjust the data import steps.
- An overview of all problems is available in tab Steps.
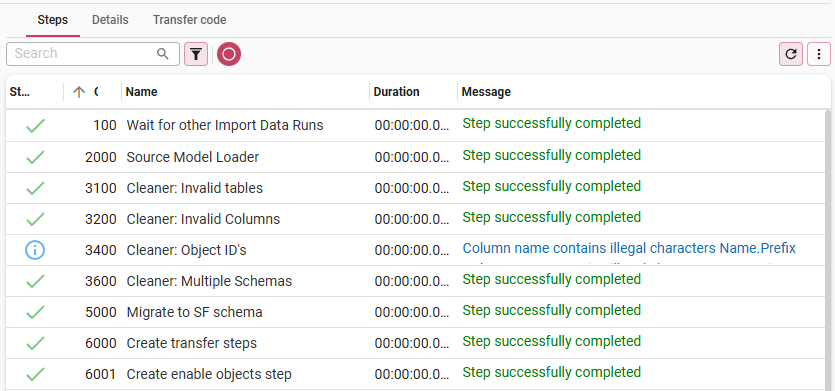 If necessary, analyze the errors in the Steps tab
If necessary, analyze the errors in the Steps tab- The full error message for a problem is available in tab Details > Message.
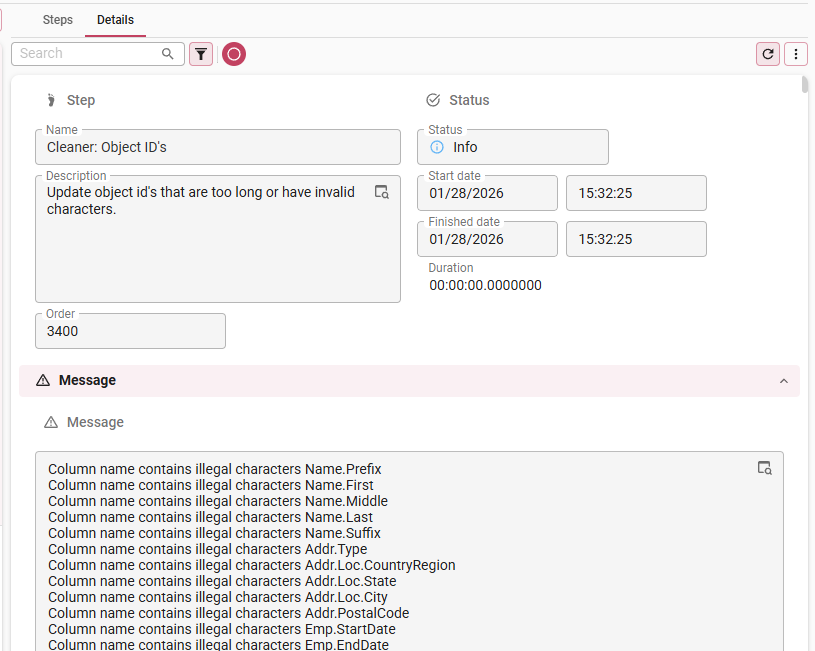 The full error message is available in tab Details > Message
The full error message is available in tab Details > Message- The generated SQL for analysis of a failed data import is available in tab Transfer code. If the import was successful, the generated SQL was removed to avoid storage of a very large data volume in the Thinkwise Upcycler.
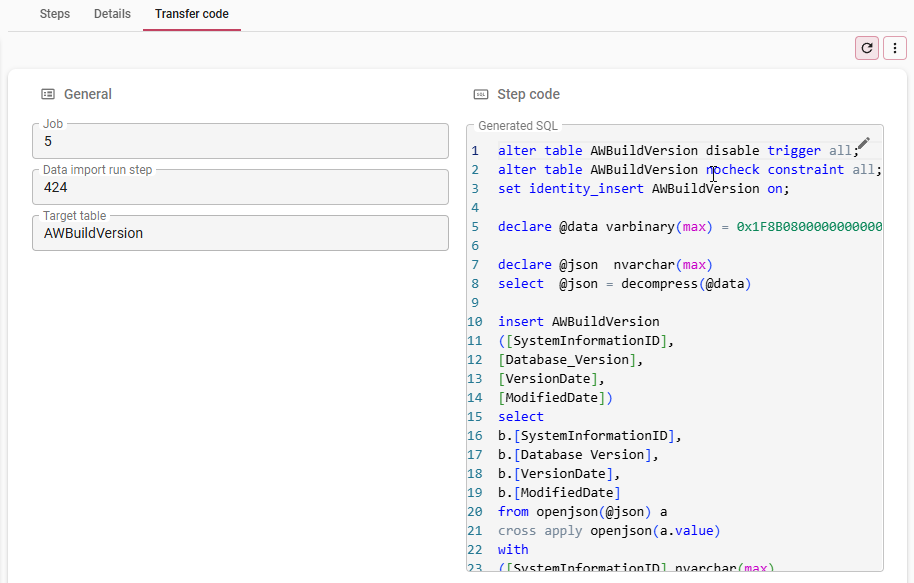 The generated SQL for a failed data import
The generated SQL for a failed data import
9. Inspect your application
- Start your application. It will now have data.
- Inspect your application to see if you still want to improve anything in the upcycle process.
10. Enrich your application
Now that your application is running with data, you can enhance it with bulk updates if necessary.
To support you in this step, Enrichment runs are available. Enrichments are a way to make mass changes to an application that would be unfeasible to do by hand.
- For general information on the enrichment run, see Introduction to enrichment runs.
- The Upcycler contains several predefined enrichments. For an overview, see Available enrichments and further.
- To fine-tune the available enrichment steps, see Fine-tune the enrichment steps.
- To create custom steps for your own Upcycler, see Create custom enrichment steps.
- If necessary, program your own enrichment steps. See Programming an enrichment.
First, execute an enrichment analysis. This will execute the enrichment analysis steps as defined in your Technology Upcycler, where necessary overruled by steps at the Application level. The run will produce enrichment action steps.
menu Upcycle > Enrichment runs > tab Application
- Select your application.
- Navigate to tab Analysis steps.
- Execute the Execute enrichment analysis
task.
- Enter the Branch.
- Press Execute.
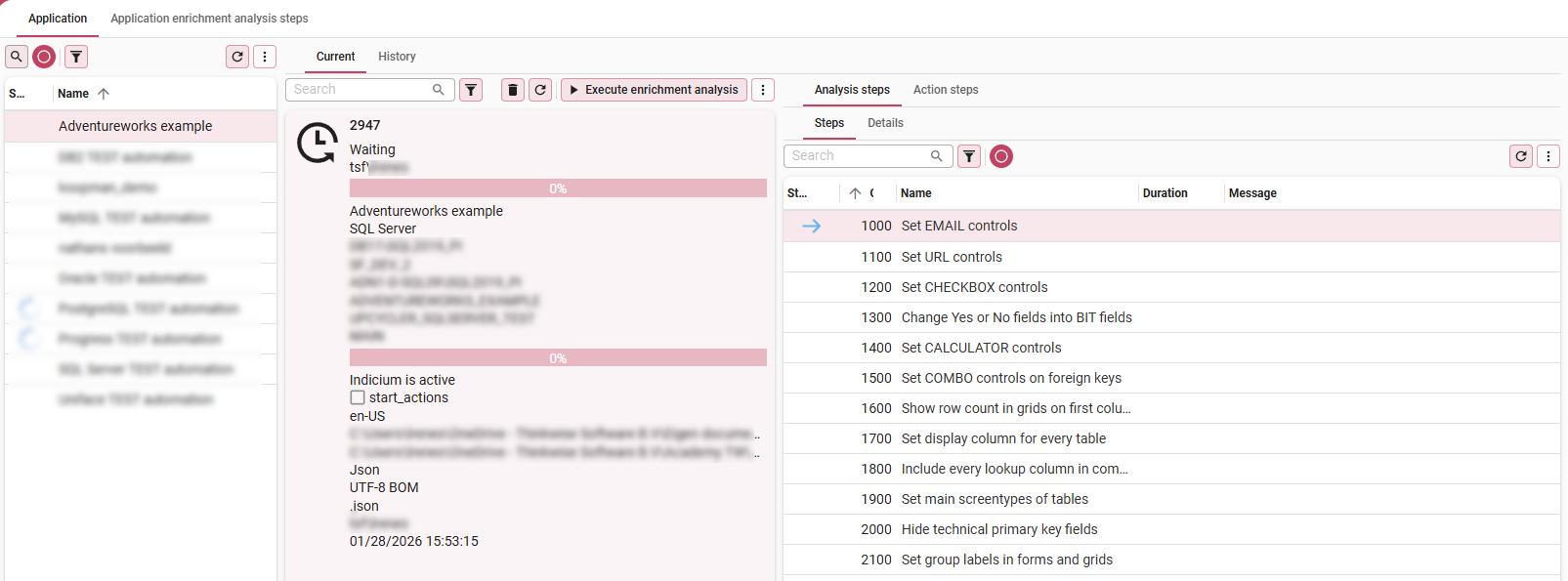 Execute the enrichment analysis steps
Execute the enrichment analysis steps
Then, execute the enrichment actions. This will execute the enrichment action steps that were produced by the analysis run.
- Navigate to tab Action steps.
- Select
or deselect
the steps you wish to execute.
- Execute the Execute enrichment actions
task.
- Answer 'Yes' to the question: "Do you want to execute task Execute enrichment actions?'.
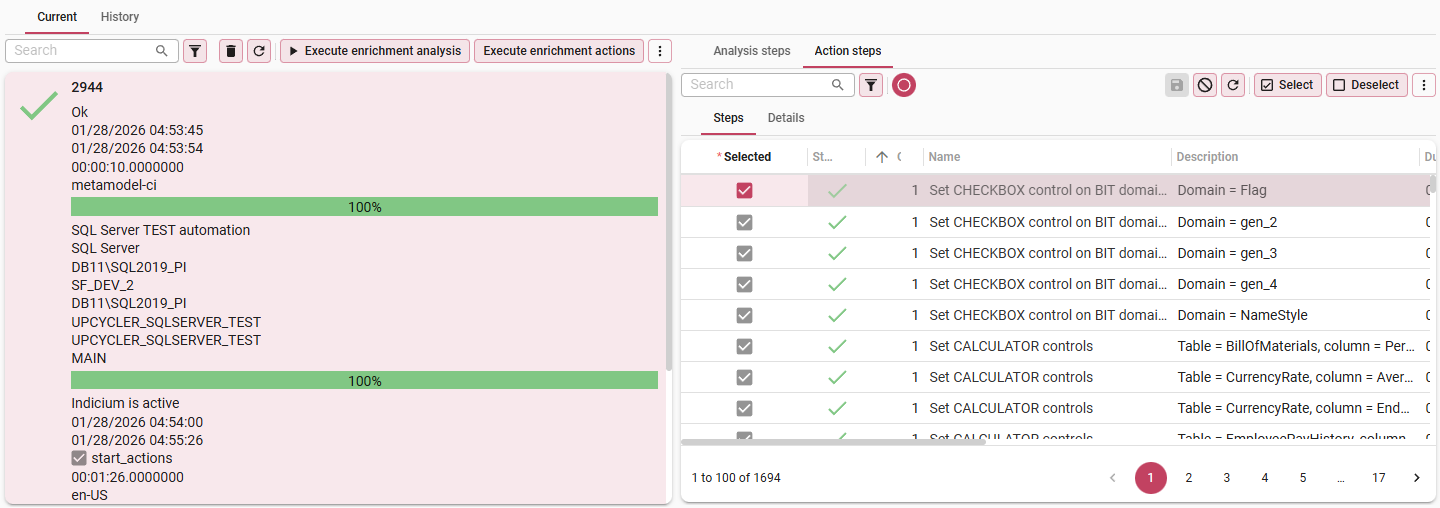 Execute the enrichment action steps
Execute the enrichment action steps
11. Inspect the enrichments
Check the database, Software Factory, and your end-application whether the enrichment actions in the model and data have been executed as expected.
12. Plan towards a full-featured application
If the upcycle process has finished, make a plan for turning your upcycled application into a full-featured Thinkwise application.
Fine-tune an Upcycler for your application
If your upcycle run needs improvement, you can fine-tune the Technology Upcycler you are using for your legacy application.
Even if you think that an improvement is valuable to all applications in this technology, it is best to try it on your specific application first.
menu Upcycle > Upcycle runs
- Select your application.
- Open tab Application upcycle steps.
- Add upcycle steps specific to your application, modify generic steps, or deactivate steps.
In tab List, you can check the status:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Base status | The status of the step at the Technology level. - Generic - the step has not been modified for this technology. - Modified - the generic step has been modified for this technology. - Specific - the step is specific for this technology and has no underlying generic step. |
| Current status | The status of the step at the Application level. - Inherited - the step has not been modified for this application. - Modified - the step has been modified for this application. - Specific - the step has been added specifically for this application. |
In tab Form, the following settings are available:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the step. |
| Active | Only active steps will be executed and shown by the default prefilters. |
| Order no | The order in which the steps will be executed. |
| Reason | The reason why you are creating a variation on a step. This field becomes available when you add or modify a step. |
| Description | The purpose of the step's functionality. |
| Step code | The SQL code that is executed for this step. |
If you have made a change and wish to revert it to the original technology upcycle step, use the
Revert to Technology upcycle step task.
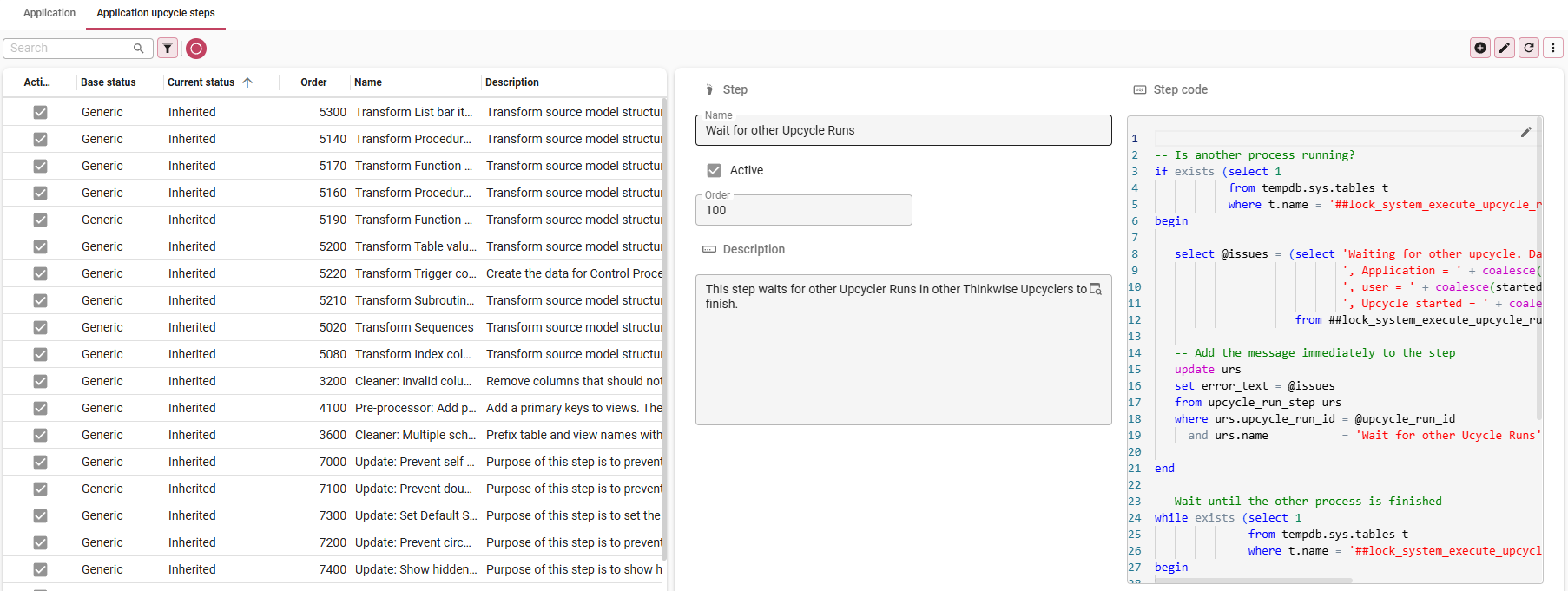 Fine-tune the Application upcycle steps
Fine-tune the Application upcycle steps
Re-run the upcycle
After finetuning the steps, you can rerun the Upcycler.
- In the Software Factory, delete the model that the Thinkwise Upcycler has created earlier for this application.
- Open the Thinkwise Upcycler (menu Upcycle > Upcycle runs).
- Select your application.
- Execute the Execute upcycle
task.
Fine-tune the data import
menu Upcycle > Data import runs
- Select your application.
- Open tab Generic data import steps.
- Add data import steps specific to your application, modify generic steps, or deactivate steps.
In tab List, you can check the status:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Base status | The status of the step at the Technology level. - Generic - the step has not been modified for this technology. - Modified - the generic step has been modified for this technology. - Specific - the step is specific for this technology and has no underlying generic step. |
| Current status | The status of the step at the Application level. - Inherited - the step has not been modified for this application. - Modified - the step has been modified for this application. - Specific - the step has been added specifically for this application. |
In tab Form, the following settings are available:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the step. |
| Active | Only active steps will be executed and shown by the default prefilters. |
| Order no | The order in which the steps will be executed. |
| Reason | The reason why you are creating a variation on a step. This field becomes available when you add or modify a step. |
| Description | The purpose of the step's functionality. |
| Step code | The SQL code that is executed for this step. |
If you have made a change and wish to revert it to the original technology data import step, execute the
Revert to Technology data import step task.
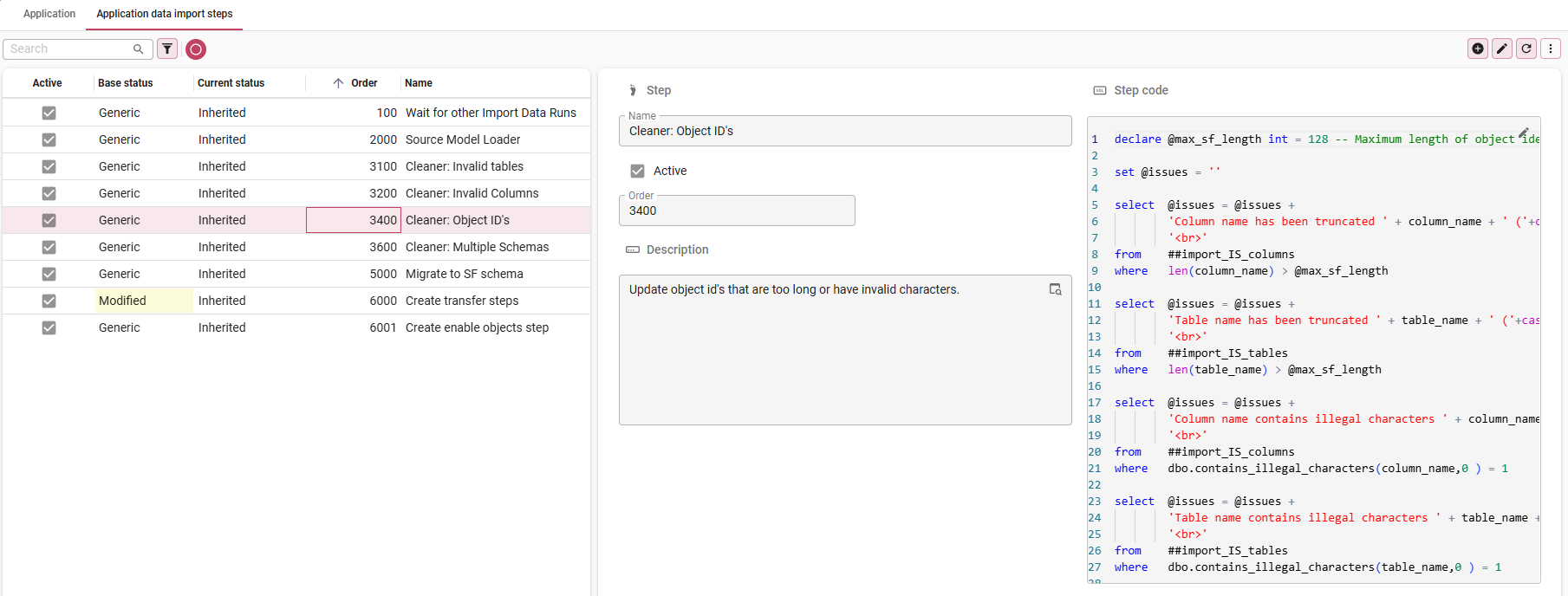 Fine-tune the data import steps
Fine-tune the data import steps
Re-run the data import
-
For re-running the data import, you need a generated database with empty tables. This can be achieved in two ways:
- With your database management tool, delete all records from all tables in your application database. This can be complicated because of the referential integrity constraints between tables.
- With your database management tool, drop the application database.
-
Create a fresh database in the Software Factory.
-
Open the Thinkwise Upcycler (menu Upcycle > Data import runs).
-
Select your application.
-
Execute the Execute data import
task.
Fine-tune the enrichment steps
menu Upcycle > Enrichment runs
- Select your application.
- Navigate to the tab Generic enrichment analysis steps.
- Add enrichment analysis steps specific to your application, modify generic steps or deactivate steps.
If an enrichment analysis step uses an AI enrichment, you must configure its settings to make it work.
In tab List, you can check the status:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Base status | The status of the step at the Technology level. - Generic - the step has not been modified for this technology. - Modified - the generic step has been modified for this technology. - Specific - the step is specific for this technology and has no underlying generic step. |
| Current status | The status of the step at the Application level. - Inherited - the step has not been modified for this application. - Modified - the step has been modified for this application. - Specific - the step has been added specifically for this application. |
In tab Form, the following settings are available:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the step. |
| Active | Only active steps will be executed and shown by the default prefilters. |
| Order no | The order in which the steps will be executed. |
| Reason | The reason why you are creating a variation on a step. This field becomes available when you add or modify a step. |
| Description | The purpose of the step's functionality. |
| Model query | The SQL code executed against the model for this step. |
| Data query | The SQL code executed against the data for this step. |
| AI Instruction | The instruction that contains the rules and guidelines that the AI should follow. |
If you have made a change and wish to revert it to the original technology data import step, execute the
Revert to technology enrichment analysis step task.
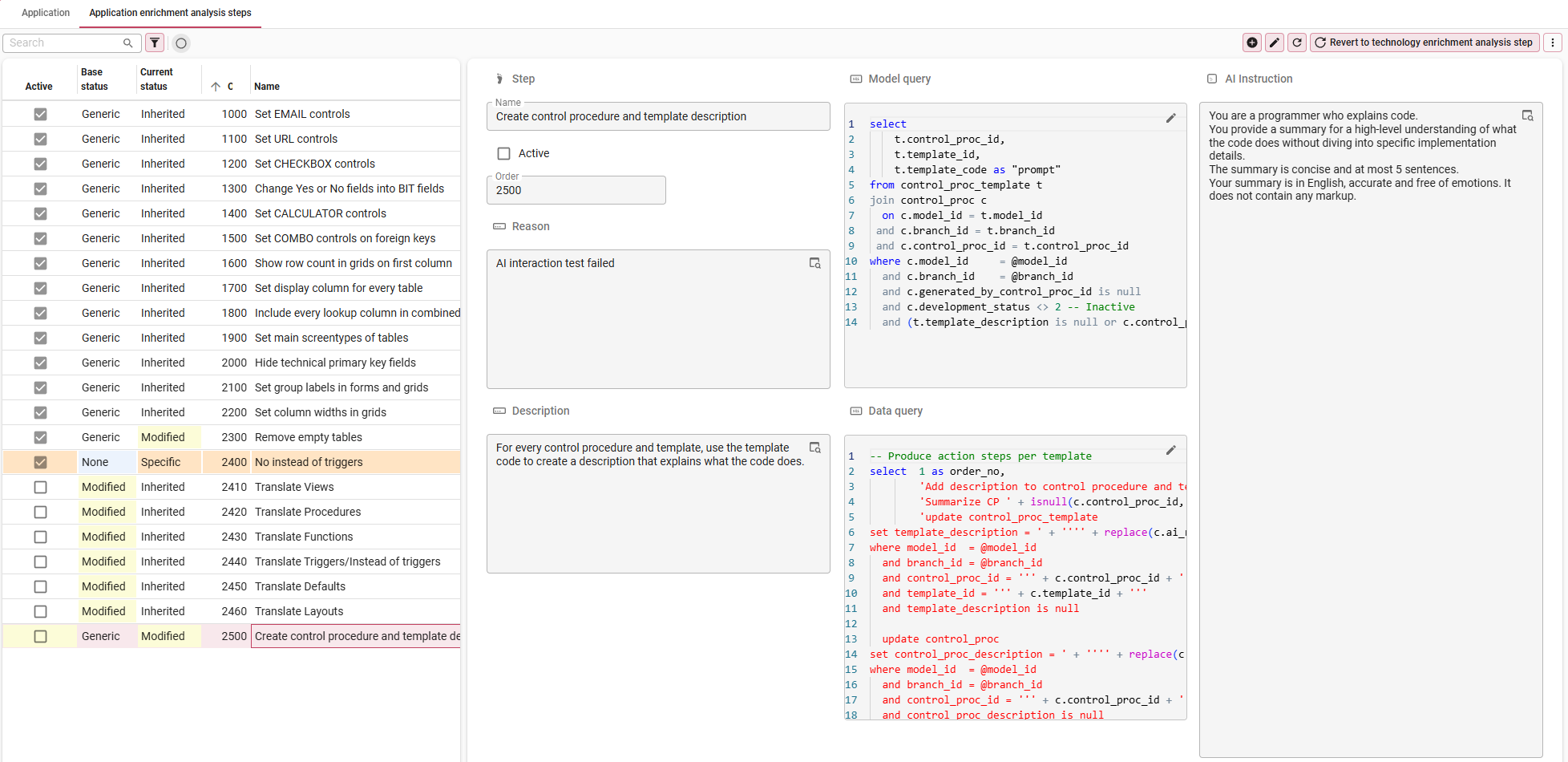 Fine-tune enrichment steps
Fine-tune enrichment steps
Configure an AI enrichment step
To configure an AI enrichment step:
menu Upcycle > Enrichment runs > tab Generic enrichment analysis steps
- Select the AI enrichment step.
- In the Form, add the rules and guidelines that the AI must follow to the field AI Instruction.
Providing more instructions generally leads to a better result. The generic AI instruction can be modified to fit every technology. - Name a column in your Model query as "prompt", to provide the AI with a prompt to use. The value of this column will be used to generate a response.
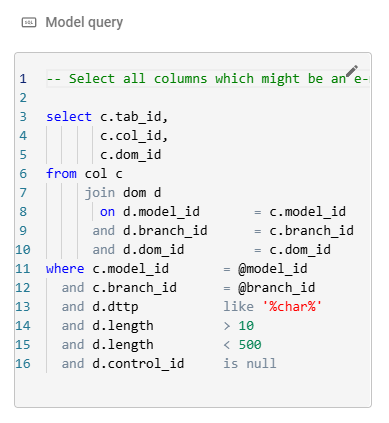 In this example, the column
In this example, the column template_code will be used as the prompt
Retrieve the AI enrichment result
To retrieve the results of the model query execution and the AI result, you can open the @json variable using the T-SQL function openjson().
The @json variable has the usual Application connector result structure, with the addition of an ai_result property in the Result list.
Note that ai_result may not be a named column inside the model query,
as this column will be automatically appended by the Upcycler after receiving a response from the AI.
For example, to select all data from the previously mentioned model query, you can use the following query:
select t3.*
from openjson(@json) t1 -- main json
cross apply openjson(a.value) t2 -- result[]
cross apply openjson(b.value) -- resultSet[]
with (
control_proc_id nvarchar(max),
template_id nvarchar(max),
template_code nvarchar(max),
ai_result nvarchar(max)
) t3
Using this data, you can specify enrichment action steps with the ai_result value. Use other steps as a reference for this.
Re-run the enrichment analysis
You can re-run the enrichment analysis without consequences until it produces the desired results.
- Create a fresh database in the Software Factory.
- Open the Thinkwise Upcycler (menu Upcycle > Enrichment runs).
- Select your application.
- In tab Analysis steps, execute the Execute enrichment analysis
task.
Be extremely careful when running the resulting enrichment actions. They can change both the model and the data. Therefore, create a new branch for your model and a backup of the data before running the actions.
- In tab Action steps, execute the Execute enrichment actions
task.
Create your own Upcycler
The Thinkwise Upcycler comes with Upcyclers for a number of technologies. If no Upcycler is available for the technology you need, you can add your own.
Only create your own Upcycler if you have sufficient knowledge of the technology, the legacy application, and the Thinkwise platform. Contact Thinkwise or one of our Certified Partners for advice on creating a new Upcycler.
1. Extract the model and data
When you are building your own Technology Upcycler, it might be necessary to create scripts for the Thinkwise Extractor as well. However, not all Technology Upcyclers use the files the Thinkwise Extractor produces, and for Platform Upcyclers, it can be more convenient to use the platform's export facilities.
Therefore, you first need to decide how to extract the model and the data from your legacy application.
-
The legacy technology that needs to be upcycled is a database - The easiest way is to use the Thinkwise Extractor. If the database system supports the Information Schema, it is the recommended way since it will result in maximum reuse of generic steps in the Upcycler. If not, use the proprietary catalog tables of the database system.
-
There needs to be one script per table in the catalog or Information Schema. You can use the scripts delivered with the Thinkwise Extractor as examples.
-
Each technology needs a script for extracting the data. You can use the pre-delivered scripts for the supported technologies as examples.
The default structure of the folders is:
The Extractor's folder structure
-
-
The legacy technology that needs to be upcycled is a platform - Investigate whether your platform has an export functionality for the model information and if you comprehend its resulting file(s). The alternative is to use the Thinkwise Extractor to extract the tables in which the application is defined.
2. Create a new technology in the Upcycler
If the technology you need is not available by default in the Thinkwise Upcycler, you can add one.
menu Definition > Technology upcyclers
- Add
a new Upcycler.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the technology. |
| Description | A short description of the technology, for example, for which versions of the technology you are creating this Upcycler. |
| Logo | The technology's logo. |
| Active | Only active technologies will be shown by the default prefilter. |
| Default model file type | Type of data in the model file, provides a default for the application. |
| Default model file extension | Extension of the model file, provides a default for the application. |
| Default model file encoding | Encoding of the model file, provides a default for the application. |
| Default data file type | Type of data in the model file, provides a default for the application. |
| Default data file extension | Extension of the data files, provides a default for the application. |
| Default data file encoding | Encoding of the data files, provides a default for the application. |
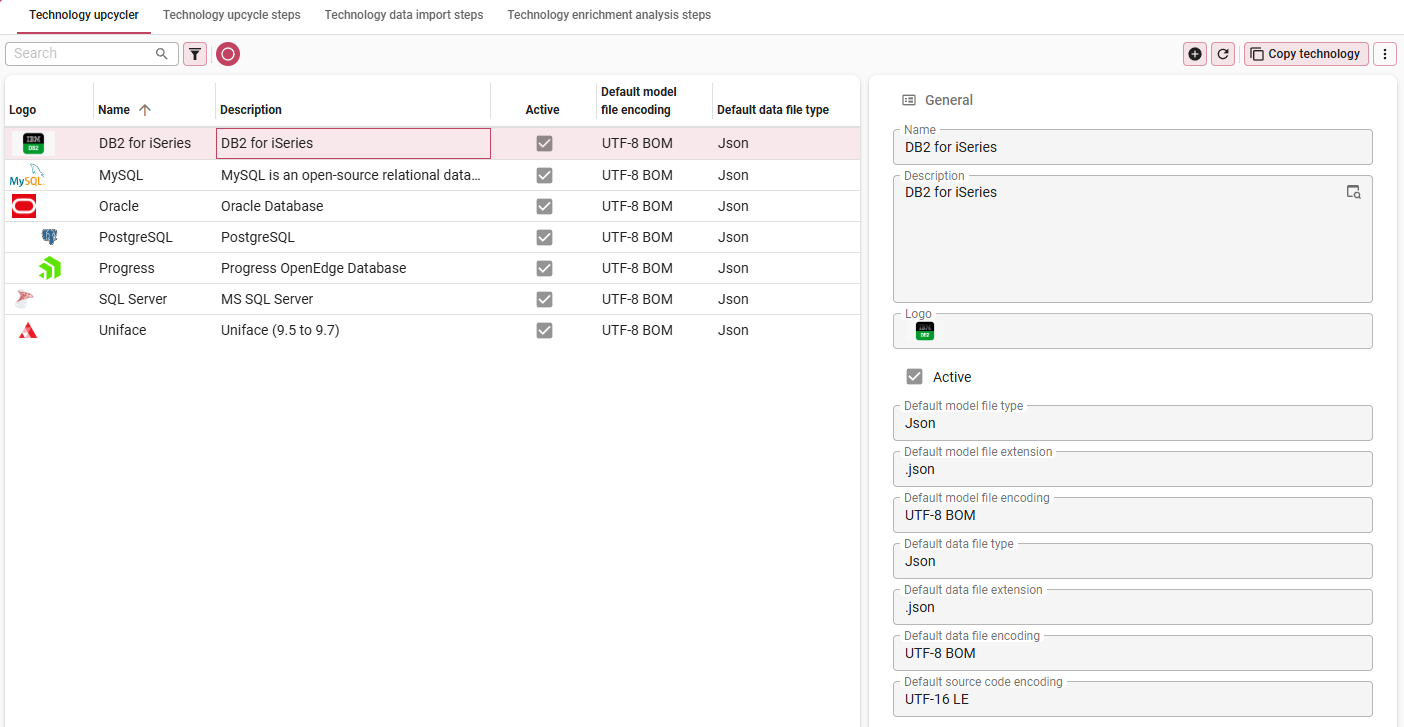 Add a new Technology Upcycler
Add a new Technology Upcycler
3. Add the Upcycle steps
menu Definition > Technology upcyclers > tab Technology upcycle steps
On opening, tab List shows the steps that have been inherited from the Generic level.
- In tab Form, Add
new steps specific to your technology or modify generic steps to make them work for your technology. You can also disable steps. Use the Upcyclers delivered by Thinkwise as examples. The modified fields turn yellow.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the step. |
| Active | Only active steps will be executed and shown by the default prefilters. |
| Status | The status of the step at this Technology level. - Generic - the step has not been modified for this technology. - Modified - the generic step has been modified for this technology. - Specific - the step this specific for the technology and has no underlying generic step. |
| Technology | The technology to which this step belongs. |
| Order no | The order in which the steps will be executed. |
| Reason | The reason why you are creating a variation on a step. This field becomes available when you add or modify a step. |
| Description | The purpose of step's functionality. |
| Step code | The SQL code that is executed for this step. |
If you have made a change and wish to revert it to the generic upcycle step, execute the
Revert to generic upcycle step task.
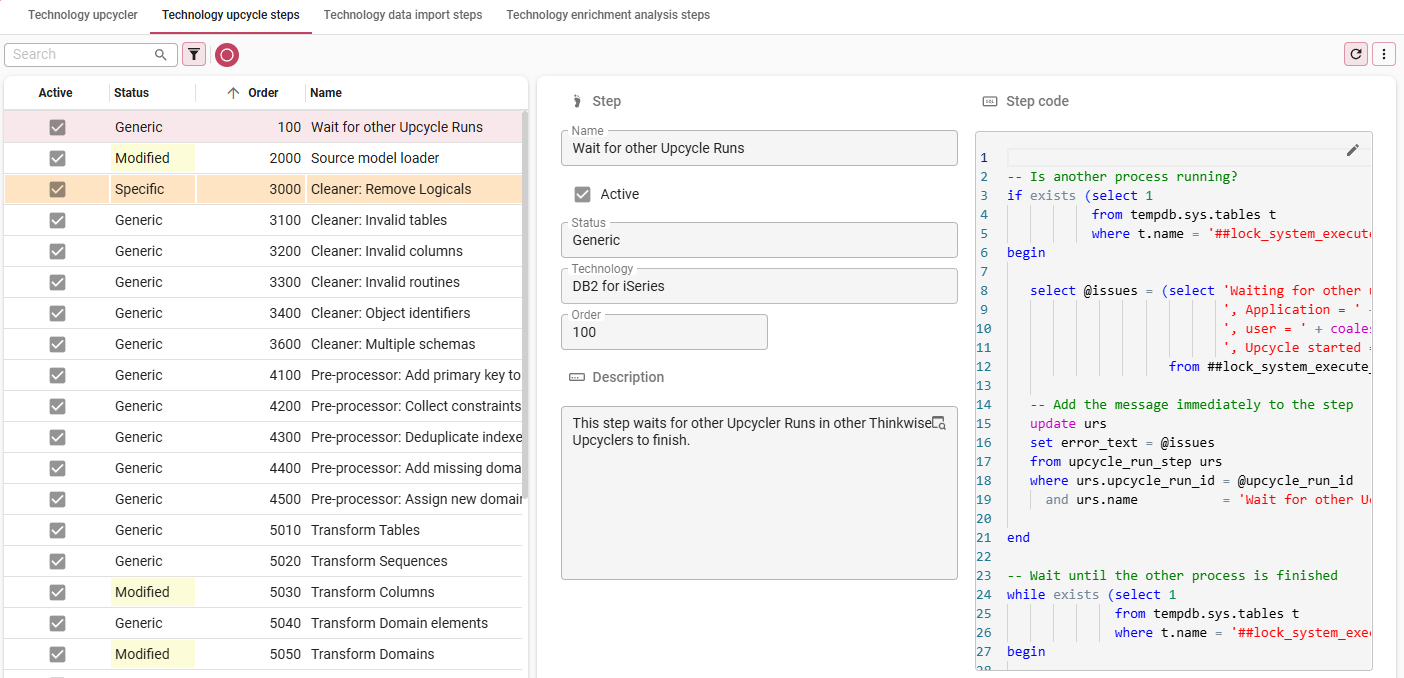 Add upcycle steps to your Upcycler
Add upcycle steps to your Upcycler
4. Test your Upcycler
Before continuing to data migration, test your Upcycler thoroughly.
Before testing it with your full legacy application, find or create a small demo application.
5. Create custom data import steps
Data can be imported into the Upcycler from any file storage type available in the Thinkwise Platform. You can set the file storage type in IAM, in the menu Authorization > Applications > tab General settings > tab File storage locations. Select the application THINKWISE_UPCYCLER, navigate to tab File storage location, and set the file storage type.
To create or modify import steps:
menu Definition > Technology upcyclers > tab Technology data import steps
On opening, tab List shows the steps that have been inherited from the Generic level.
-
In tab Form, Add
new steps that are specific to your technology or modify generic steps to make them work for your technology. You can also disable steps. Use the Upcyclers delivered by Thinkwise as examples.
- For a Technology Upcycler based on the Information Schema, you only need minimal changes on top of the generic steps. Ideally, only the translation of data types needs to be customized.
- For a Technology Upcycler for a platform, it may be necessary to put more effort into the data import steps, although it will be less than for the upcycle steps.
The modified fields turn yellow.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the step. |
| Active | Only active steps will be executed and shown by the default prefilters. |
| Status | The status of the step at the Technology level. - Generic - the step has not been modified for this technology. - Modified - the generic step has been modified for this technology. - Specific - the step is specific for this technology and has no underlying generic step. |
| Technology | The technology to which this step belongs. |
| Order no | The order in which the steps will be executed. |
| Reason | The reason why you are creating a variation on a step. This field becomes available when you add or modify a step. |
| Description | The purpose of step's functionality. |
| Step code | The SQL code that is executed for this step. |
If you have made a change and wish to revert it to the generic upcycle step, execute the
Revert to generic upcycle step task.
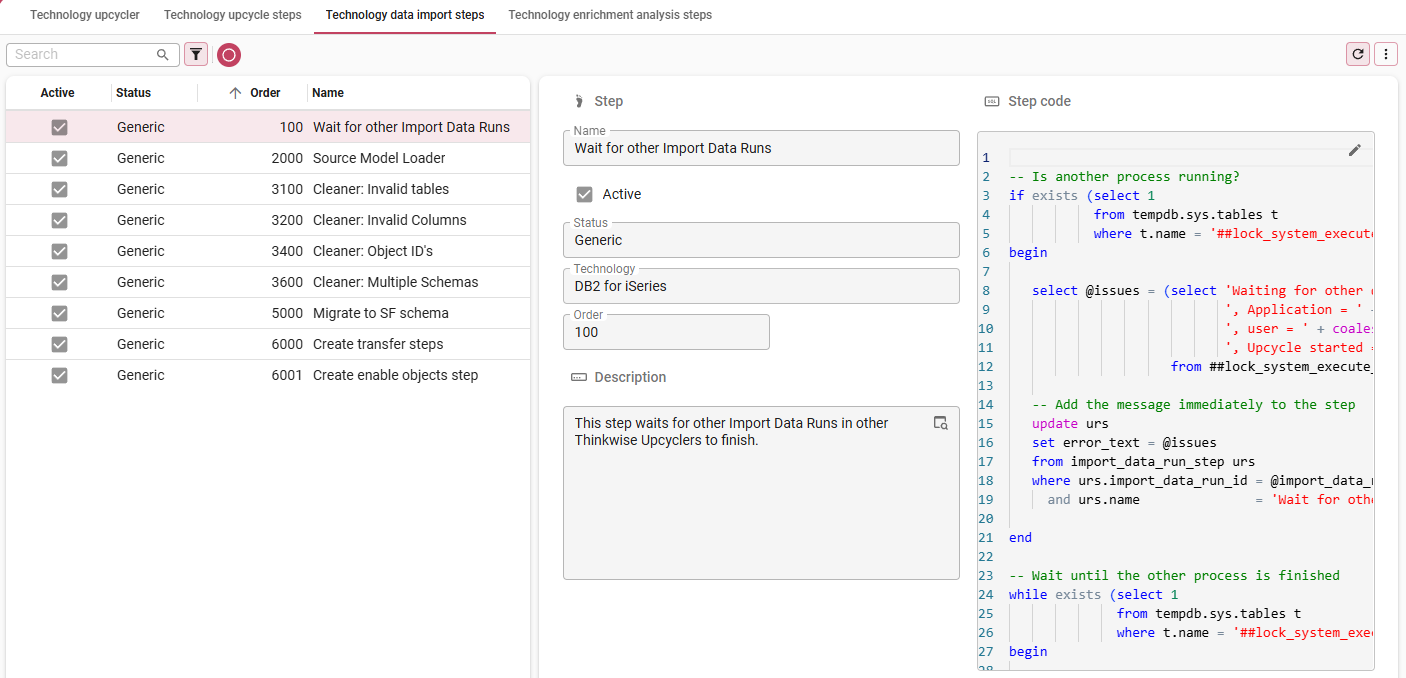 Create data import steps
Create data import steps
6. Test the custom data import steps
Test your customized data import steps thoroughly.
Before processing a full production database, test a smaller set first.
7. Create custom enrichment steps
menu Definition > Technology upcyclers > tab Technology enrichment analysis steps
On opening, tab List shows the steps that have been inherited from the Generic level.
- In tab Form, Add
new steps specific to your technology or modify generic steps to make them work for your technology. You can also disable steps. Use the Upcyclers delivered by Thinkwise as examples. The modified fields turn yellow.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the step. |
| Active | Only active steps will be executed and shown by the default prefilters. |
| Status | The status of the step at the Technology level. - Generic - the step has not been modified for this technology. - Modified - the generic step has been modified for this technology. - Specific - the step is specific for this technology and has no underlying generic step. |
| Technology | The technology to which this step belongs. |
| Order no | The order in which the steps will be executed. |
| Description | The purpose of the step's functionality. |
| Model query | The SQL code that is executed against the model for this step. |
| Data query | The SQL code that is executed against the data for this step. |
If you have made a change and wish to revert it to the generic upcycle step, execute the
Revert to generic enrichment analysis step task.
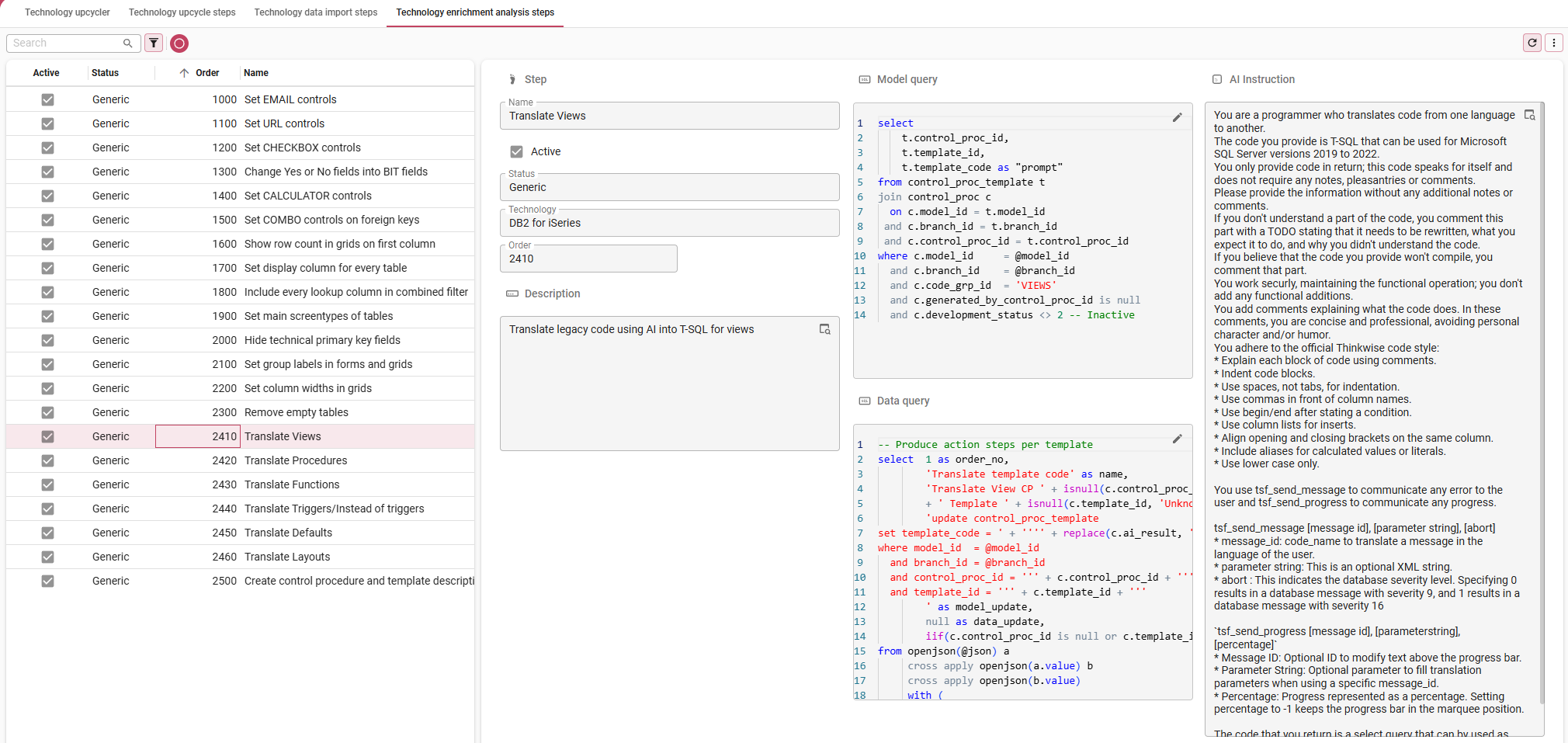 Create custom enrichment steps
Create custom enrichment steps
8. Test the custom enrichment steps
Test your customized enrichment steps thoroughly.
You can re-run the enrichment analysis without consequences until it produces the desired result. Before processing a full production database, test a smaller set first.
Be extremely careful when running the resulting enrichment actions. They can change both the model and the data. Therefore, create a new version of your model and a backup of the data before running the actions.