Universal theme
Introduction to Universal theme
You can use themes in the Universal UI to define the overall look and feel of the interface. You can set up a font type, color palette, and other style properties. For each theme, you can configure a Light and a Dark mode. You can apply a different theme to each of your applications.
If you use the Windows GUI for your application, see Classic theme (Windows GUI).
Create a theme
To create a theme for the Universal UI:
menu User Interface > Themes
-
Select Add
and enter a theme name.
-
Select Universal as Theme type. Windows GUI To set up a classic theme, see Classic theme (Windows GUI).
-
Enter a Description.
-
Set the Default theme to Dark or Light. A user can switch between the dark and light mode in the application, so settings are available for both modes. Users can change their preferences in the profile menu. For more information, see Theme and localization.
-
Upload a Theme picture for both the Light and Dark mode. This image is used as a background image in the application.
-
Select the Fit for the background:
- Tiled - The image is repeated horizontally and vertically across the entire screen, like a pattern, without scaling or distortion. Empty spaces are filled with the background color.
- Center - The image is centered. Empty spaces are filled with the main color.
- Fit - The image is resized so it fits within the screen, without being cropped or distorted. Empty spaces are filled with the main color.
- Stretch - The image is resized to fill the entire screen in width and height. The image may be distorted (stretched wider or taller).
- Fill - The image is resized to cover the screen completely. Parts of the image may be cropped.
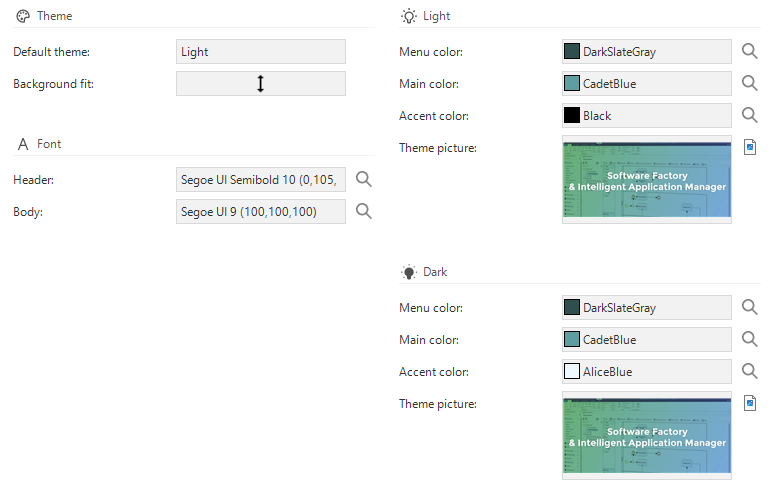 Universal theme settings
Universal theme settings
Set up a font
You can select an existing font or add a new one. The selected font face and size are used for the headers and body of the interface; the font color and style are ignored.
To add a new font:
menu User Interface > Themes > group Font
- Select the lookup control
.
- In the lookup pop-up, go to the tab Form.
- Select the Add
button.
- Select a Font face, Font size, and Color.
- Optional. The font name is automatically generated and available in the field Font. You can change this if desired.
Set up colors
The following colors are available to style an application, for both Dark and Light mode:
- Menu color - The color of the menu and top bar. If the menu color is not set, the main color is used. You can use menu colors to differentiate between applications or to match the color of your company logo. Check if the main and accent colors have sufficient contrast with the menu color and backgrounds used in both light and dark modes to ensure optimal readability.
- Main color - The primary color refers to the color that appears most frequently in the application.
- Accent color - The accent color refers to the color used to accent key parts of the user interface. For example, the background color of badges.
You can select an existing color or add a new one.
To add a new color:
menu User Interface > Themes > group Light/Dark
- Select the lookup control
.
- In the lookup pop-up, select one of the following:
- Basic color
- Custom color - select the color in the color picker and select Add to Custom Colors.
Change the application icon and title
By default, an application is provided with a Thinkwise icon and title. You can change this to customize your application.
The Universal folder contains three icons:
favicon.ico- The browser tab icon.logo.png- The shortcut icon on your screen (resolution 192x192)logo-512.png- The shortcut icon on your screen (resolution 512x512)
Your browser decides whether to use logo.png or logo-512.png, based on the resolution.
To change the logo and title:
When you replace the Universal UI with a newer build, exclude the manifest.json file and your icons, or they will be overwritten.
- Open the
Universalfolder. - Change the icons.
- If you added icons with another name, point to the new icons in the
manifest.json. - Here, you can also change the application title.
See also:
Comfortable and compact mode in the Universal UI
It is important to find the right balance between content and whitespace in your application. Proper use of whitespace improves comprehension, legibility, and focus and can help guide the user through the interface.
By default, the Universal UI uses comfortable mode. This mode offers more spacing between elements, creating a clear and legible interface. Some applications or use cases are less suited for this mode. For example, when an application displays large amounts of data that users need to scan, view, and compare. You can use compact mode in the Universal UI to display more data on the screen.
See the table below for the differences between these two modes.
| Setting | Compact | Comfortable |
|---|---|---|
| Font size | 14px | 14px |
| Grid row height | 36px | 44px |
| Pivot grid row height | 36px | 36px |
| Spacing | 4px | 8px |
Users can switch between comfortable and compact mode in their profile settings. For more information, see Theme and localization.
You can set the default mode for your users in the config.json file.
Use the following code:
"spacingMode": "compact"
If you do not define spacingMode:
compactis used for desktop.comfortableis used for touch devices.
You can customize the appearance of screen components in the Universal UI, for example by adjusting grid and form settings. For more information, see Settings for subjects.
Custom CSS in the Universal UI
- Adding custom CSS by renaming the
custom.sample.cssfile tocustom.cssin the public folder of the Universal UI is deprecated. You can add Custom CSS for a web domain in IAM to customize login pages and application-wide styling. - The Custom CSS file configured per web domain in IAM takes precedence over the existing
custom.cssfile of the Universal UI. If a Custom CSS file is added in IAM, the entirecustom.cssfile of the Universal UI is ignored. If no Custom CSS file is uploaded in IAM, the Universal UI uses its originalcustom.cssfile.