Development environment reference architecture
Introduction to the development environment reference architecture
Purpose:
Used by developers for writing, building, and initially verifying new code or features.
The Thinkwise Software Factory is the production environment for your developers.
User Types:
- Software Developers: Primary users for code creation and modification.
- Technical Leads/Architects: Occasionally validate implementation approaches or perform initial reviews.
Access Method:
- Typically via local user accounts or developer-managed credentials.
- No external authentication (such as OpenID) required; focus is on ease of access for rapid iteration.
Data:
- Synthetic, mock, or minimal datasets for functionality checks.
- Usually isolated from real, acceptance, or production data.
Typical Activities:
- Code writing and debugging
- Unit testing and initial functional checks
- Code reviews and developer integration
Tools:
- Thinkwise Software Factory
- SSMS
Development environment requirements
A development environment should be set up with as few restrictions as possible and requires the following conditions to function properly:
- Minimal Restrictions – Allow smooth debugging, integration, and testing of components.
- AI Configuration – Requires an active (paid) API key to access AI services such as OpenAI or other platforms.
- Database Requirements – Installation of Microsoft SQL Server is required:
- Version: Standard or Enterprise
- Full Text Search must be enabled
- Security (SSL/TLS) – The environment must support SSL:
- Browsers impose restrictions on HTTP, leading to reduced performance compared to HTTPS.
- Supported certificate types:
- Standard SSL certificate
- Wildcard certificate
- Self-signed certificate (acceptable for internal testing)
- Thinkwise Windows GUI for development – Requires at least 500MB RAM memory per user.
- Indicium Service Account – A dedicated service account is required for running Indicium with:
- Write permissions on the Indicium directory
- Access rights to both the IAM database and the application database
- Secure management in accordance with the organization’s identity and access policies
Cloud
Architecture and connections with 4 developers or less
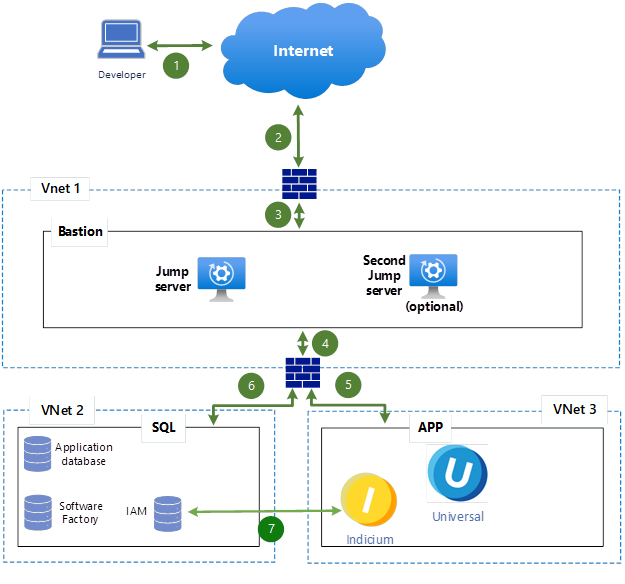 Cloud development environment reference architecture
Cloud development environment reference architecture
Connections:
- Developer to Internet – Connects to the bastion environment via public internet.
- Internet to External Firewall – Incoming connection hits an external firewall.
- External Firewall to Bastion (Jump Server) – Traffic passes into the secure bastion environment.
- Bastion to Internal Firewall – Traffic moves through an internal firewall into protected VNets.
- Bastion to App Server (VNet 3) – Secure connection to application servers.
- Bastion to SQL Server (VNet 2) – Secure connection to SQL Server.
- App Server to SQL Server – Application servers connect to the SQL server.
Summary of commonly used ports:
| Service | Typical Port Numbers |
|---|---|
| RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) | TCP 3389 |
| HTTPS (secured web/admin) | TCP 443 |
| SQL Server | TCP 1433 |
Architecture and connections with 5 developers or more
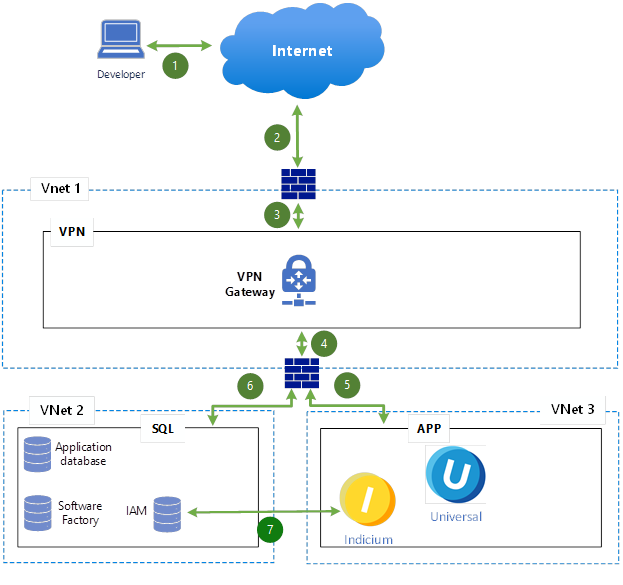 Cloud development environment reference architecture
Cloud development environment reference architecture
Connections:
- Developer to Internet – Connects to the bastion environment via public internet.
- Internet to External Firewall – Incoming connection hits an external firewall.
- External Firewall to Bastion (VPN) – Traffic passes into the bastion environment (VPN).
- Bastion to Internal Firewall – Traffic moves through an internal firewall into protected VNets.
- Bastion to App Server (VNet 3) – Secure connection to application servers.
- Bastion to SQL Server (VNet 2) – Secure connection to SQL Server.
- App Server to SQL Server – Application servers connect to the SQL server.
Summary of commonly used ports:
| Service | Typical Port Numbers |
|---|---|
| HTTPS (secured web/admin) | TCP 443 |
| SQL Server | TCP 1433 |
Sizing (hardware cloud)
Recommended specifications (cloud):
| Component | Azure | AWS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VM (optional) | DS11 v2 (2 vCPUs, 14 GiB) | m6i.large (2 vCPU, 16 GiB) | E2-standard-4 (4vCPU, 16 GB) |
| SQL | Azure Managed Instance (4vCores, 20 GB) | AWS RDS db.m5.xlarge (4 vCPU, 16GB) | SQL server 4 vCPU, 16 GB |
| Indicium & Universal | AppService Basic B2 | Elastic Beanstalk t3.large | Cloud Run (Memory: 1 GB) Storage Bucket Class data: Default Class Standard |
Cloud environment setup
For more information about setting up a cloud environment, see:
On Premise
Architecture and connections
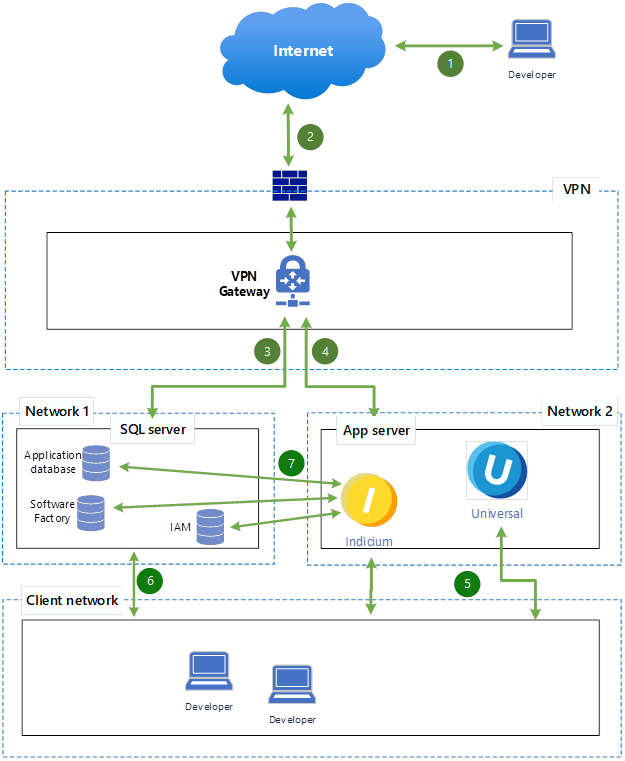 On-premise development environment reference architecture
On-premise development environment reference architecture
Connections:
- Developer to Internet – The developer initiates a connection to the VPN gateway through the Internet.
- Internet to Firewall – The request reaches a firewall that filters inbound VPN traffic.
- Firewall to VPN Gateway – Traffic allowed by firewall rules passes to the VPN Gateway.
- VPN Gateway to Internal Networks – After authentication, the VPN Gateway routes traffic securely into internal networks.
- Client Network to Application Server (Network 2) – Developers or clients from internal networks access applications hosted on the Application Server.
- Client Network to SQL Server (Network 1) – Direct interaction from developer/client machines to the SQL Server (management tools, database queries).
- App Server to SQL Server – Application Server accesses the databases hosted on SQL Server.
Summary of commonly used ports:
| Service | Typical Port Numbers |
|---|---|
| HTTPS (secured web / VPN SSL) | TCP 443 |
| SQL Server | TCP 1433 |
| RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) | TCP 3389 |
Sizing (hardware on premise)
Recommended hardware specifications (IIS Server):
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU | 4 vCPUs |
| Memory | 16 GB RAM |
| Storage | 100–200 GB |
| OS | Windows Server 2019/2022 |
Recommended hardware specs (SQL Server):
| Component | Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU | 4 vCPUs |
| Memory | 16 GB (1–5 developers) 32 GB (6–10 developers) |
| Storage | Windows/SQL installation: 200 GB SQL Data: 200 GB SQL Log: 100 GB Best practice is to separate the installation, data and log locations |
| OS | Windows Server 2019/2022 |
| SQL | SQL Server 2019/2022 Standard or Enterprise |
On-premise environment setup
For more information about setting up an on-premise environment, see: